2023.9.4 追記
先日 Lambda の go1.x ランタイムのサポートが 2023/12/31 に終了する案内がありましたが、その対応については本記事では未反映となります。別記事で取り上げる予定です。
はじめに
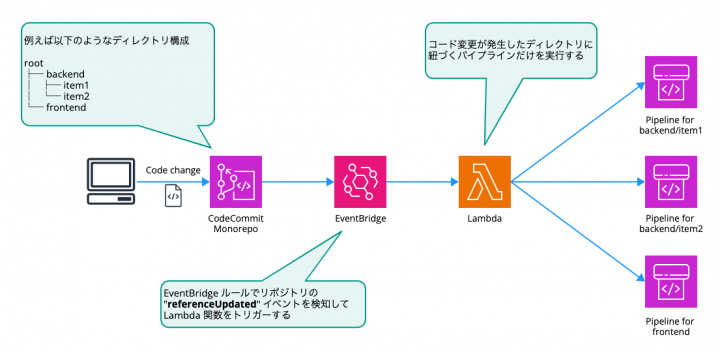
モノレポ構造の CodeCommit リポジトリを運用しており、かつパイプラインが CodePipeline 前提の場合、パイプラインの実行制御はどうするのかという課題があると思います。アプリケーションの各機能がサブディレクトリ単位で管理されている場合、以下のような方式が考えられます。
- パイプラインもサブディレクトリ単位で構築する
- どのサブディレクトリでコードの変更があったかを検知する
- 変更があったサブディレクトリに対応するパイプラインだけを実行する
実際にはもっと複雑なディレクトリ構成になっていると思いますし、そう単純でもないと思いますが、概ねこのようなアプローチを取るのが一般的である認識です。しかし記事執筆時点では、この動作は CodePipeline ではサポートされていません。今回はこのロジックを Go 言語で実装してみました。
構成図
CDK コード
周辺リソースは CDK で作ります。CDK は TypeScript で書いています。
コンテキスト
まず cdk.json で必要な context を定義します。pipelines はパイプライン名に使う識別子とそれに紐づくディレクトリのマッピング情報です。なおコンテキストは app.node.tryGetContext() で取得して使いますが、以降のコード例では省略しています。
{
...
"context": {
"serviceName": "monorepo-test",
"repositoryName": "test-repo",
"branch": "feature",
"pipelines": [
{
"name": "item1",
"path": "backend/item1",
},
{
"name": "item2",
"path": "backend/item2",
},
{
"name": "frontend",
"path": "frontend",
},
]
}
}
CodeCommit リポジトリ
既存リポジトリを使用する想定なので、fromRepositoryName または fromRepositoryArn でインポートします。
// Get codecommit repository codecommit.Repository.fromRepositoryName(this, "CodeCommitRepository", repositoryName);
Lambda ロール
以下のようなポリシーでロールを作ります。
// Create role for pipeline trigger function
const pipelineHandlerRole = new iam.Role(this, "PipelineHandlerRole", {
roleName: `${serviceName}-pipeline-handler-role`,
assumedBy: new iam.ServicePrincipal("lambda.amazonaws.com"),
inlinePolicies: {
["PipelineHandlerRoleAdditionalPolicy"]: new iam.PolicyDocument({
statements: [
new iam.PolicyStatement({
resources: [`arn:aws:codepipeline:${this.region}:${this.account}:*`],
actions: [
"codepipeline:GetPipeline",
"codepipeline:ListPipelines",
"codepipeline:StartPipelineExecution",
"codepipeline:StopPipelineExecution",
],
}),
],
}),
},
});
Dead Letter Queue
Lambda に渡す DLQ を作ります。
// Create DLQ
const deadLetterQueue = new sqs.Queue(This, "PipelineHandlerQueue", {
queueName: `${serviceName}-pipeline-handler-queue`,
encryption: sqs.QueueEncryption.SQS_MANAGED,
enforceSSL: true,
removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.DESTROY,
retentionPeriod: Duration.days(7),
});
Lambda 関数
Lambda 関数は前述の DLQ に加え、バージョンとエイリアスも設定します。
// Create lambda function for pipeline handler
const pipelineHandler = new lambda.Function(this, "PipelineHandler", {
functionName: `${serviceName}-pipeline-handler`,
description: "Receives codecommit code change events and starts pipelines for specific directories.",
code: lambda.Code.fromAsset("src/lambda/pipeline-trigger", {
bundling: {
image: lambda.Runtime.GO_1_X.bundlingImage,
command: [
"bash",
"-c",
[
"export GOCACHE=/tmp/go-cache",
"export GOPATH=/tmp/go-path",
"GOOS=linux go build -o /asset-output/main main.go",
].join(" && "),
],
},
}),
handler: "main",
architecture: lambda.Architecture.X86_64,
runtime: lambda.Runtime.GO_1_X,
role: pipelineHandlerRole,
logRetention: logs.RetentionDays.THREE_DAYS,
environment: {
PIPELINES: JSON.stringify(pipelines),
},
currentVersionOptions: {
removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.RETAIN,
},
deadLetterQueueEnabled: true,
deadLetterQueue: deadLetterQueue,
reservedConcurrentExecutions: 1,
retryAttempts: 2,
});
// Update function alias
const pipelineHandlerAlias = new lambda.Alias(scope, "PipelineHandlerAlias", {
aliasName: "live",
version: pipelineHandler.currentVersion,
});
// Add permission
codeCommitRepository.grantRead(pipelineHandlerAlias);
とりわけ重要なのが bandling で、デプロイ前に実行するビルドコマンドを定義します。この場合 Docker イメージでのビルドを想定しているので、Docker が動く環境である必要があります。私の環境だとパーミッションエラーが発生したので、GOPATH と GOCACHE を /tmp 下に変更してから linux ビルドを実行しています (冒頭に書いた内容は別記事で紹介します)
bundling: {
image: lambda.Runtime.GO_1_X.bundlingImage,
command: [
"bash",
"-c",
[
"export GOCACHE=/tmp/go-cache",
"export GOPATH=/tmp/go-path",
"GOOS=linux go build -o /asset-output/main main.go",
].join(" && "),
],
},
また、環境変数でパイプラインのマッピング情報を渡します。
environment: {
PIPELINES: JSON.stringify(pipelines),
},
EventBridge ルール
CodeCommit リポジトリに変更が発生した時に Lambda 関数を発火するためのイベントパターンを作ります。
referenceUpdated を拾う以下のようなイベントパターンが必要なので、
{
"detail-type": ["CodeCommit Repository State Change"],
"resources": ["arn:aws:codecommit:<region-name>:<account-id>:<repository-name>"],
"source": ["aws.codecommit"],
"detail": {
"event": ["referenceUpdated"],
"referenceName": ["<branch-name>"]
}
}
このように書きます。
// Create event rule for repository state change
const pipelineHandlerEventRule = new events.Rule(this, "PipelineHandlerEventRule", {
enabled: true,
ruleName: `${serviceName}-pipeline-handler-rule`,
eventPattern: {
source: ["aws.codecommit"],
detailType: ["CodeCommit Repository State Change"],
resources: [codeCommitRepository.repositoryArn],
detail: {
event: ["referenceUpdated"],
referenceName: [branch],
},
},
});
最後にイベントのターゲットに Lambda 関数のエイリアスを設定します。
pipelineHandlerEventRule.addTarget(new events_targets.LambdaFunction(pipelineHandlerAlias));
Lambda コード
全体としては以下のようなコードです。
// main.go
package main
import (
"context"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"log"
"os"
"strings"
"github.com/aws/aws-lambda-go/events"
"github.com/aws/aws-lambda-go/lambda"
"github.com/aws/aws-sdk-go-v2/aws"
"github.com/aws/aws-sdk-go-v2/config"
"github.com/aws/aws-sdk-go-v2/service/codecommit"
"github.com/aws/aws-sdk-go-v2/service/codepipeline"
)
// Information about a pipeline such as its name and target path
type PipelineInfo struct {
Name string `json:"name"`
Path string `json:"path"`
Type string `json:"type"`
}
// Information about the event detail in CodeCommit
type CodeCommitDetail struct {
Event string `json:"event"`
RepositoryName string `json:"repositoryName"`
RepositoryId string `json:"repositoryId"`
ReferenceType string `json:"referenceType"`
ReferenceName string `json:"referenceName"`
ReferenceFullName string `json:"referenceFullName"`
CommitId string `json:"commitId"`
OldCommitId string `json:"oldCommitId"`
BaseCommitId string `json:"baseCommitId"`
SourceCommitId string `json:"sourceCommitId"`
DestinationCommitId string `json:"destinationCommitId"`
MergeOption string `json:"mergeOption"`
ConflictDetailsLevel string `json:"conflictDetailsLevel"`
ConflictResolutionStrategy string `json:"conflictResolutionStrategy"`
}
// Global AWS SDK configuration
var cfg aws.Config
// Initializes the AWS SDK configuration
func init() {
var err error
cfg, err = config.LoadDefaultConfig(context.TODO())
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot load aws sdk config: %v", err)
}
}
// Retrieves the files that have changed between last 2 commits
func getChangedFiles(ctx context.Context, repositoryName string, oldCommitId string, commitId string) ([]string, error) {
var (
paths []string
nextToken *string
)
client := codecommit.NewFromConfig(cfg)
for {
resp, err := client.GetDifferences(ctx, &codecommit.GetDifferencesInput{
RepositoryName: aws.String(repositoryName),
BeforeCommitSpecifier: aws.String(oldCommitId),
AfterCommitSpecifier: aws.String(commitId),
NextToken: nextToken,
})
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("cannot get file diff: %w", err)
}
for _, diff := range resp.Differences {
if diff.AfterBlob != nil && diff.AfterBlob.Path != nil {
paths = append(paths, *diff.AfterBlob.Path)
}
}
nextToken = resp.NextToken
if nextToken == nil {
break
}
}
return paths, nil
}
// Determines which pipelines should be triggered based on the changed paths
func getPipelines(paths []string, pipelines []PipelineInfo) map[string]struct{} {
targets := make(map[string]struct{})
prefix := strings.Split(os.Getenv("AWS_LAMBDA_FUNCTION_NAME"), "pipeline-handler")[0]
pathMap := make(map[string]struct{})
for _, path := range paths {
pathMap[path] = struct{}{}
}
for _, pipeline := range pipelines {
pipelineName := prefix + pipeline.Name + "-pipeline"
for path := range pathMap {
if strings.HasPrefix(path, pipeline.Path) {
targets[pipelineName] = struct{}{}
break
}
}
}
return targets
}
// Starts a CodePipeline execution
func startPipeline(ctx context.Context, pipelineName string) error {
client := codepipeline.NewFromConfig(cfg)
resp, err := client.StartPipelineExecution(ctx, &codepipeline.StartPipelineExecutionInput{
Name: aws.String(pipelineName),
})
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("cannot start pipeline \"%s\": %w", pipelineName, err)
}
log.Printf("pipeline started: %s, executionId: %s\n", pipelineName, *resp.PipelineExecutionId)
return nil
}
// Lambda function handler that triggers pipelines based on changes in CodeCommit repositories
func handleRequest(ctx context.Context, event events.CloudWatchEvent) error {
pipelineConfig := os.Getenv("PIPELINES")
if pipelineConfig == "" {
return fmt.Errorf("cannot get PIPELINES environment variable")
}
var pipelines []PipelineInfo
if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(pipelineConfig), &pipelines); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("cannot unmarshal PIPELINES environment variable: %w", err)
}
var detail CodeCommitDetail
if err := json.Unmarshal(event.Detail, &detail); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("cannot unmarshal event detail: %w", err)
}
paths, err := getChangedFiles(ctx, detail.RepositoryName, detail.OldCommitId, detail.CommitId)
if err != nil {
return err
}
targetPipelines := getPipelines(paths, pipelines)
for pipelineName := range targetPipelines {
if err := startPipeline(ctx, pipelineName); err != nil {
return err
}
}
log.Printf("all pipelines started successfully")
return nil
}
// Entrypoint of the Lambda function
func main() {
lambda.Start(handleRequest)
}
init
init では初期化プロセスとして AWS SDK の設定を読み込みます。
func init() {
var err error
cfg, err = config.LoadDefaultConfig(context.TODO())
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("cannot load aws sdk config: %v", err)
}
}
getChangedFiles
getChangedFiles 関数では client.GetDifferences() で 2 つのコミット間の差分を抽出し、
resp, err := client.GetDifferences(ctx, &codecommit.GetDifferencesInput{
RepositoryName: aws.String(repositoryName),
BeforeCommitSpecifier: aws.String(oldCommitId),
AfterCommitSpecifier: aws.String(commitId),
NextToken: nextToken,
})
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("cannot get file diff: %w", err)
}
取得したパス情報をスライスに詰めます。
for _, diff := range resp.Differences {
if diff.AfterBlob != nil && diff.AfterBlob.Path != nil {
paths = append(paths, *diff.AfterBlob.Path)
}
}
なお、ページネーションを考慮し NextToken のチェックを行っています。
nextToken = resp.NextToken
if nextToken == nil {
break
}
getPipelines
getPipelines では変更されたファイルに基づいて開始するパイプラインを決定します。ここでなぜ値が必要ないのに map を使っているかですが、キーの一意性を保証したい、かつ自前でそのロジックを書くより高速だからです。
pathMap := make(map[string]struct{})
for _, path := range paths {
pathMap[path] = struct{}{}
}
for _, pipeline := range pipelines {
pipelineName := prefix + pipeline.Name + "-pipeline"
for path := range pathMap {
if strings.HasPrefix(path, pipeline.Path) {
targets[pipelineName] = struct{}{}
break
}
}
}
startPipeline
startPipeline 関数では受け取った名前のパイプラインを実行します。
resp, err := client.StartPipelineExecution(ctx, &codepipeline.StartPipelineExecutionInput{
Name: aws.String(pipelineName),
})
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("cannot start pipeline \"%s\": %w", pipelineName, err)
}
handleRequest
handleRequest 関数ではまず環境変数から取得したパイプラインのマッピング情報をパースします。
var pipelines []PipelineInfo
if err := json.Unmarshal([]byte(pipelineConfig), &pipelines); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("cannot unmarshal PIPELINES environment variable: %w", err)
}
受け取った CodeCommit イベントの詳細情報をパースします。
var detail CodeCommitDetail
if err := json.Unmarshal(event.Detail, &detail); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("cannot unmarshal event detail: %w", err)
}
getChangedFiles で変更されたファイルのパスを取得します。
paths, err := getChangedFiles(ctx, detail.RepositoryName, detail.OldCommitId, detail.CommitId)
if err != nil {
return err
}
getPipelines で実行するパイプラインを決定し、それぞれを startPipeline 関数で実行します。
targetPipelines := getPipelines(paths, pipelines)
for pipelineName := range targetPipelines {
if err := startPipeline(ctx, pipelineName); err != nil {
return err
}
}
main
最後に、handleRequest 関数を Lambda 関数のハンドラーとして登録します。
func main() {
lambda.Start(handleRequest)
}
おわりに
コミット間の差分情報を解析して複数のパイプラインの実行を制御する Lambda 関数を Go で実装してみました。CDK との組み合わせで、パイプラインのマッピング情報をコンテキストで管理できる点が気に入っています。



![[Laravel] テストケースが全てPassしているのに、終了ステータスが1になってしまう件](https://iret.media/wp-content/themes/clp_media/img/common/home-thumbnail_360x240.png)