はじめに
OSS の IAM (Identity and Access Management) ソフトウェアである Keycloak を AWS 環境上に構築する機会がありましたので紹介します。
⻑くなったので記事を 3 つに分割しており、今回は最後です。ECS on Fargate で動作する Quarkus ベースの Keycloak クラスタを CDK を⽤いて実装します。
- 選定
- コンテナのビルド
- 実装とデプロイ (これ)
最終的な実装サンプルはこちらになります。
構成
以下の構成図の通りに CDK でリソースを構築します。
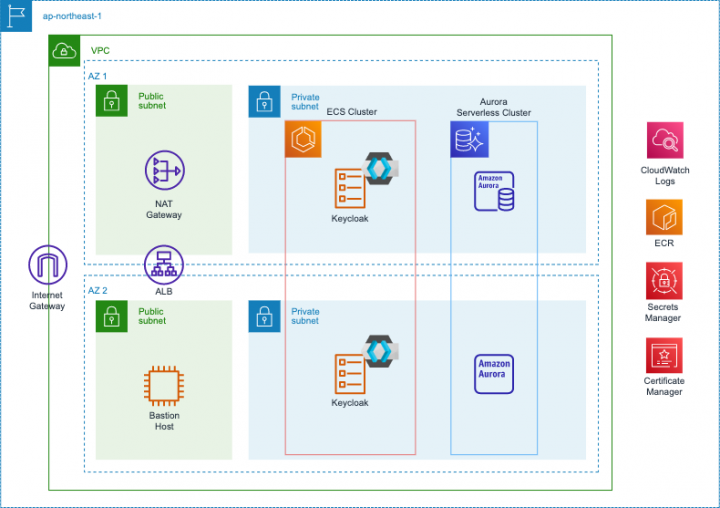
スタック
以下のようにスタックを分割しました。
| スタック名 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| CertificateStack | 証明書をデプロイするスタック。Keycloak 以外のスタックと連携することも想定し、証明書 ARN を SSM パラメータストアに登録する |
| KeycloakStack | コンテナイメージ, VPC, Aurora サーバーレス V2, ECS on Fargate, 踏み台 EC2 インスタンスを構成するメインスタック |
KeycloakStack では、Aurora サーバーレス V2 などステートフルなリソースや VPC など永続的なリソースと、Amazon ECS などのステートレスなリソースを同じスタックで定義しています。
スタック間の依存を発⽣させないために極⼒スタックを分割しないという考え⽅と、少なくともステートフルなリソースとステートレスなリソースは分割すべきという考え⽅、どちらもあると思います。今回は前者を選択しています。
実装
実装例をコードを交えて紹介します (GitHub 上のコードから⾃前メソッドなどを省き、少し簡略化したも
のを載せています)
証明書
まずは ACM 証明書のデプロイです。これだけスタックを別にしているのは、認証認可基盤だけでなくアプ
リケーション本体でもこの証明書をアタッチできるようにするためです。スタック間の依存を最⼩限にする
ため、SSM パラメーターストアに登録する⽅式を選択しました。
// Wildcard certificate
const certificate = new acm.Certificate(this, "Certificate", {
certificateName: "certificate",
domainName: "dev-feature.example.com",
subjectAlternativeNames: ["*.dev-feature.example.com"],
validation: acm.CertificateValidation.fromDns(
route53.HostedZone.fromLookup(this, "HostedZone", {
domainName: "example.com",
})
),
});
// Put parameter: certificateArn
new ssm.StringParameter(this, "CertificateParameter", {
parameterName: "dev/feature/certificateArn",
stringValue: certificate.certificateArn,
});
ただし、この証明書を us-east-1 でデプロイする想定はないため、CloudFront での使⽤については視野に⼊れていません。
VPC
VPC の構築です。今回 Secret の取得は NAT Gateway 経由を想定しているので、プライベートサブネットには NAT Gateway を配置します。機会があれば VPC エンドポイント経由も CDK でコード化してみたいです。
DB クレデンシャルを取得するための通信はクリティカルな部類だと思うので、本来であれば VPC エンドポイントを使うか NAT Gateway を冗⻑化すべきと考えます。
パブリックサブネットの情報は ALB に渡しますし、プライベートサブネットの情報も RDS に渡しますので、それぞれ vpc.selectSubnet()で取得しておきます。
// Base Vpc
const vpc = new ec2.Vpc(this, "VPC", {
ipAddresses: ec2.IpAddresses.cidr("10.0.0.0/16"),
enableDnsHostnames: true,
enableDnsSupport: true,
natGateways: 1,
maxAzs: 2,
subnetConfiguration: [
{
name: "Public",
subnetType: ec2.SubnetType.PUBLIC,
cidrMask: 24,
},
{
name: "Private",
subnetType: ec2.SubnetType.PRIVATE_WITH_EGRESS,
cidrMask: 24,
},
],
});
const vpcPublicSubnets = vpc.selectSubnets({ subnetType:
ec2.SubnetType.PUBLIC });
const vpcPrivateSubnets = vpc.selectSubnets({ subnetType:
ec2.SubnetType.PRIVATE_WITH_EGRESS });
Aurora サーバーレス V2
DB は容易にスケーリングを設定できる Aurora サーバーレス V2 を選択し、ユーザー認証が特定の時間帯に
集中しても対応できるようにします。コードは以下となります。
const mysqlEngine = rds.DatabaseClusterEngine.auroraMysql({
version: rds.AuroraMysqlEngineVersion.VER_3_02_0,
});
// Database cluster parameter group
const dbClusterParameterGroup = new rds.ParameterGroup(this,
"DBClusterParameterGroup", {
engine: mysqlEngine,
description: `Cluster parameter group for aurora-mysql8.0 for
${serviceName} authentication infrastructure`,
parameters: {
slow_query_log: "1",
},
});
dbClusterParameterGroup.bindToCluster({});
(dbClusterParameterGroup.node.defaultChild as
rds.CfnDBClusterParameterGroup).dbClusterParameterGroupName =
`${serviceName}-db-cluster-pg-aurora-mysql8`;
// Database instance parameter group
const dbInstanceParameterGroup = new rds.ParameterGroup(this,
"DBInstanceParameterGroup", {
engine: mysqlEngine,
description: `Instance parameter group for aurora-mysql8.0 for
${serviceName} authentication infrastructure`,
});
dbInstanceParameterGroup.bindToInstance({});
(dbInstanceParameterGroup.node.defaultChild as
rds.CfnDBParameterGroup).dbParameterGroupName = `${serviceName}-db-instancepg-aurora-mysql8`;
// Database subnet group
const dbSubnetGroup = new rds.SubnetGroup(this, "DBSubnetGroup", {
subnetGroupName: `${serviceName}-db-subnet-group`,
description: `${serviceName}-db-subnet-group`,
removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.DESTROY,
vpc: vpc,
vpcSubnets: vpcPrivateSubnets,
});
// Database security group
const dbSecurityGroupName = `${serviceName}-db-security-group`;
const dbSecurityGroup = new ec2.SecurityGroup(this, "DBSecurityGroup", {
securityGroupName: dbSecurityGroupName,
description: dbSecurityGroupName,
vpc: vpc,
allowAllOutbound: true,
});
Tags.of(dbSecurityGroup).add("Name", dbSecurityGroupName);
// Database credential
const dbSecret = new asm.Secret(this, "DBSecret", {
secretName: `${serviceName}-db-secret`,
description: "Credentials for database",
generateSecretString: {
generateStringKey: "password",
excludeCharacters: " % +~`#$&*()|[]{}:;?!'/@\"\\",
passwordLength: 30,
secretStringTemplate: JSON.stringify({ username: "admin" }),
},
});
// Aurora Serverless v2
const dbCluster = new rds.DatabaseCluster(this, "DBCluster", {
engine: mysqlEngine,
clusterIdentifier: `${serviceName}-db-cluster`,
instanceIdentifierBase: `${serviceName}-db-instance`,
defaultDatabaseName: serviceName,
deletionProtection: false,
credentials: rds.Credentials.fromSecret(dbSecret),
instanceProps: {
vpc: vpc,
vpcSubnets: vpcPrivateSubnets,
instanceType: new ec2.InstanceType("serverless"),
securityGroups: [dbSecurityGroup],
parameterGroup: dbInstanceParameterGroup,
enablePerformanceInsights: true,
},
subnetGroup: dbSubnetGroup,
parameterGroup: dbClusterParameterGroup,
backup: {
retention: Duration.days(1),
},
storageEncrypted: true,
removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.DESTROY,
copyTagsToSnapshot: true,
cloudwatchLogsExports: ["error", "general", "slowquery", "audit"],
cloudwatchLogsRetention: logs.RetentionDays.THREE_MONTHS,
});
(dbCluster.node.defaultChild as
rds.CfnDBCluster).serverlessV2ScalingConfiguration = {
minCapacity: 0.5,
maxCapacity: 4,
};
const dbListenerPort = 3306;
dbCluster.connections.allowInternally(
ec2.Port.tcp(dbListenerPort),
"Allow resources with this security group connect to database"
);
dbCluster.connections.allowFrom(
ec2.Peer.ipv4(vpc.vpcCidrBlock),
ec2.Port.tcp(dbListenerPort),
"Allow resources in VPC connect to database"
);
いくつか要点があります。まず DB クラスターパラメーターグループや DB インスタンスパラメーターグル
ープは、あとから個別に設定変更ができるようにデフォルトのものではなく個別に作成しておきます。
メインのリソースに関してルールに則って命名したいケースを想定しているため、これらについても命名を
しますが、DBParameterGroup を CloudFormation で作成する場合、以前は名前を指定することができま
せんでした。
これが 2022 年 11 ⽉からできるようになったのですが、L2 コンストラクトの props では相変わらず設定
することができないので、L1 コンストラクトにアクセスし、該当するプロパティを編集します。
以下のように defaultChild を使って内部で定義されている L1 コンストラクトにアクセスし、該当のプ
ロパティを書き換えています。
// DB クラスターパラメーターグループの名前を書き換える
(dbClusterParameterGroup.node.defaultChild as
rds.CfnDBClusterParameterGroup).dbClusterParameterGroupName =
`${serviceName}-db-cluster-pg-aurora-mysql8`;
// DB インスタンスパラメーターグループの名前を書き換える
(dbInstanceParameterGroup.node.defaultChild as
rds.CfnDBParameterGroup).dbParameterGroupName = `${serviceName}-db-instancepg-aurora-mysql8`;
DB クレデンシャルは AWS Secrets Manager や SSM パラメーターストアで扱うのがセオリーです。今回
は AWS Secrets Manager を使います。以下のようにシークレットを定義し、
const dbSecret = new asm.Secret(this, "DBSecret", {
secretName: `${serviceName}-db-secret`,
description: "Credentials for database",
generateSecretString: {
generateStringKey: "password",
excludeCharacters: " % +~`#$&*()|[]{}:;?!'/@\"\\",
passwordLength: 30,
secretStringTemplate: JSON.stringify({ username: "admin" }),
},
});
DB クラスタの credentials に渡してやります。
const dbCluster = new rds.DatabaseCluster(this, "DBCluster", {
...
credentials: rds.Credentials.fromSecret(dbSecret),
...
};
なお、以下のように rds.Credentials.fromGeneratedSecret() を使うことで、Secret をインスタンス化せずに直接設定することもできます。
aws_rds.Credentials.fromGeneratedSecret("admin")
今回は secretName や description を⾃前で指定したい場合のテンプレ的なコードにしたい意味もあったので、敢えて Secret を定義してからrds.Credentials.fromSecret(dbSecret)で渡す⽅法を採⽤しています。
Aurora サーバーレス V2 のスケーリング設定も、現状 L2 コンストラクトでは直接設定できないようなので、以下のように L1 コンストラクトにアクセスしてキャパシティを定義するようにしました。
(dbCluster.node.defaultChild as
rds.CfnDBCluster).serverlessV2ScalingConfiguration = {
minCapacity: 0.5,
maxCapacity: 4,
}
あるあるですが、通常マネコンなどでログを CloudWatch Logs へ連携するように設定した場合、初期値がNever expire となる場合が多いので、油断するとログが永久に保管されてしまって無駄な課⾦が発⽣するケースがあります。
CDK の場合はこの点も考慮されており、例えば DatabaseCluster の場合はcloudwatchLogsRetention という props が⽤意されており、保管期間を設定することができます。
これはどのように実現されているかというと、裏でカスタムリソースが作成され、Lambda が起動してロググループの保管期間を⾃動で書き換えてくれます。ここまで抽象化してくれることが CDK 最⼤の強みだと思います。
同様に、S3 バケットを削除するときに中⾝をあらかじめ削除できるautoDeleteObjects というprops もあり⾮常に便利なのですが、これも裏でカスタムリソースを作成することで実現されています。
続いて Amazon ECS のコードです。少し⻑くなります。
// Get ECR repository
const containerRepository = ecr.Repository.fromRepositoryArn(
this,
"ContainerRepository",
`arn:aws:ecr:${region}:${account}:repository/${repositoryName}`
);
// Deploy container image
const tag = "latest"
new DockerImageDeployment(this, "KeycloakImageDeploy", {
source: Source.directory("src/image/keycloak"),
destination: Destination.ecr(containerRepository, { tag: tag }),
});
// Port settings
const containerPort = 8080;
const ecsPortSettings = [
{
Port: containerPort,
Protocol: ecs.Protocol.TCP,
Description: "keycloak: http",
ECSServiceConnection: false,
},
{
Port: 7800,
Protocol: ecs.Protocol.TCP,
Description: "keycloak: jgroups-tcp",
ECSServiceConnection: true,
},
{
Port: 57800,
Protocol: ecs.Protocol.TCP,
Description: "keycloak: jgroups-tcp-fd",
ECSServiceConnection: true,
},
];
// ECS cluster
const ecsCluster = new ecs.Cluster(this, "ECSCluster", {
clusterName: `${serviceName}-cluster`,
vpc: vpc,
containerInsights: true,
});
ecsCluster.node.addDependency(dbCluster);
// ECS task execution role
const ecsTaskExecutionRole = new iam.Role(this, "ECSTaskExecutionRole", {
roleName: `${serviceName}-task-execution-role`,
assumedBy: new iam.CompositePrincipal(
new iam.ServicePrincipal("ecs.amazonaws.com"),
new iam.ServicePrincipal("ecs-tasks.amazonaws.com")
),
managedPolicies:
[iam.ManagedPolicy.fromAwsManagedPolicyName("AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnl
});
// ECS task role
const ecsTaskRole = new iam.Role(this, "ECSTaskRole", {
roleName: `${serviceName}-task-role`,
assumedBy: new iam.CompositePrincipal(new iam.ServicePrincipal("ecstasks.amazonaws.com")),
});
// ECS task definition
const ecsTaskDefinition = new ecs.FargateTaskDefinition(this,
"ECSTaskDefinitionBase", {
family: `${serviceName}-task-definition`,
cpu: 1024,
memoryLimitMiB: 2048,
runtimePlatform: {
operatingSystemFamily: ecs.OperatingSystemFamily.LINUX,
cpuArchitecture: ecs.CpuArchitecture.X86_64,
},
executionRole: ecsTaskExecutionRole,
taskRole: ecsTaskRole,
});
// Keycloak credential
const userSecret = new asm.Secret(this, "UserSecret", {
secretName: `${serviceName}-user-secret`,
description: "Credentials for keycloak",
generateSecretString: {
generateStringKey: "password",
excludePunctuation: true,
passwordLength: 12,
secretStringTemplate: JSON.stringify({ username: serviceName }),
},
});
// ECS log group
const ecsLogGroup = new logs.LogGroup(this, "ECSLogGroup", {
logGroupName: `ecs/${serviceName}`,
retention: logs.RetentionDays.THREE_MONTHS,
removalPolicy: RemovalPolicy.DESTROY,
});
// ECS port mappings
const ecsPortMappings: ecs.PortMapping[] = [];
ecsPortSettings.map((param) => {
ecsPortMappings.push({
containerPort: param.Port,
protocol: param.Protocol,
});
});
// Task definition with container definition added
ecsTaskDefinition.addContainer("ECSTaskDefinition", {
containerName: serviceName,
image: ecs.ContainerImage.fromEcrRepository(containerRepository, tag),
command: ["--verbose", "start"],
secrets: {
KC_DB_PASSWORD: ecs.Secret.fromSecretsManager(dbCluster.secret!,
"password"),
KEYCLOAK_ADMIN: ecs.Secret.fromSecretsManager(userSecret, "username"),
KEYCLOAK_ADMIN_PASSWORD: ecs.Secret.fromSecretsManager(userSecret,
"password"),
},
logging: ecs.LogDrivers.awsLogs({
logGroup: ecsLogGroup,
streamPrefix: serviceName,
}),
environment: {
KC_CACHE_CONFIG_FILE: "cache-ispn-jdbc-ping.xml",
KC_DB: "mysql",
KC_DB_URL:
`jdbc:mysql://${dbCluster.clusterEndpoint.hostname}:${dbListenerPort}/${servic
KC_DB_URL_DATABASE: serviceName,
KC_DB_URL_HOST: dbCluster.clusterEndpoint.hostname,
KC_DB_URL_PORT: String(dbListenerPort),
KC_DB_USERNAME: dbUserName,
KC_HOSTNAME: domainName,
KC_HOSTNAME_STRICT_BACKCHANNEL: "true",
KC_PROXY: "edge",
},
portMappings: ecsPortMappings,
});
// Allow execution role to read the secrets
dbCluster.secret!.grantRead(ecsTaskDefinition.executionRole!);
userSecret.grantRead(ecsTaskDefinition.executionRole!);
// ECS service security group
const ecsServiceSecurityGroupName = `${serviceName}-ecs-service-securitygroup`;
const ecsServiceSecurityGroup = new ec2.SecurityGroup(this,
"ECSServiceSecurityGroup", {
securityGroupName: ecsServiceSecurityGroupName,
description: ecsServiceSecurityGroupName,
vpc: vpc,
allowAllOutbound: true,
});
Tags.of(ecsServiceSecurityGroup).add("Name", ecsServiceSecurityGroupName);
// ECS service
const ecsService = new ecs.FargateService(this, "ECSService", {
serviceName: `${serviceName}-service`,
cluster: ecsCluster,
taskDefinition: ecsTaskDefinition,
circuitBreaker: { rollback: true },
desiredCount: 2,
healthCheckGracePeriod: Duration.minutes(5),
securityGroups: [ecsServiceSecurityGroup],
enableECSManagedTags: true,
enableExecuteCommand: true,
});
// ECS allowed traffic
ecsPortSettings.map((param) => {
if (param.ECSServiceConnection) {
ecsService.connections.allowFrom(
ecsService.connections,
param.Protocol === ecs.Protocol.TCP ? ec2.Port.tcp(param.Port) :
ec2.Port.udp(param.Port),
param.Description
);
}
});
// Allow ECS service connect to database
dbCluster.connections.allowDefaultPortFrom(ecsService, "Allow ECS service
connect to database");
// ECS auto scaling capacity
const ecsAutoScaling = ecsService.autoScaleTaskCount({
minCapacity: 2,
maxCapacity: 4,
});
// ECS auto scaling by cpu utilization
ecsAutoScaling.scaleOnCpuUtilization("ECSCPUScaling", {
policyName: `${serviceName}-cpu-scaling-policy`,
targetUtilizationPercent: 80,
scaleOutCooldown: Duration.seconds(300),
scaleInCooldown: Duration.seconds(300),
});
// ECS auto scaling by schedule
ecsAutoScaling.scaleOnSchedule("ECSScalingOutBeforeOpening", {
schedule: aas.Schedule.cron({
minute: "30",
hour: "23",
weekDay: "MON-FRI",
month: "*",
year: "*",
}),
minCapacity: 2,
maxCapacity: 4,
});
ecsAutoScaling.scaleOnSchedule("ECSScalingInAfterOpening", {
schedule: aas.Schedule.cron({
minute: "30",
hour: "1",
weekDay: "MON-FRI",
month: "*",
year: "*",
}),
minCapacity: 1,
maxCapacity: 2,
});
ecsAutoScaling.scaleOnSchedule("ECSScalingOutBeforeClosing", {
schedule: aas.Schedule.cron({
minute: "0",
hour: "8",
weekDay: "MON-FRI",
month: "*",
year: "*",
}),
minCapacity: 2,
maxCapacity: 4,
});
});
ecsAutoScaling.scaleOnSchedule("ECSScalingInAfterClosing", {
schedule: aas.Schedule.cron({
minute: "0",
hour: "10",
weekDay: "MON-FRI",
month: "*",
year: "*",
}),
minCapacity: 1,
maxCapacity: 2,
});
// ALB security group
const albSecurityGroupName = `${serviceName}-alb-security-group`;
const albSecurityGroup = new ec2.SecurityGroup(this, "ALBSecurityGroup", {
securityGroupName: albSecurityGroupName,
description: albSecurityGroupName,
vpc: vpc,
allowAllOutbound: false,
});
Tags.of(albSecurityGroup).add("Name", albSecurityGroupName);
albSecurityGroup.addIngressRule(ec2.Peer.ipv4("0.0.0.0/0"),
ec2.Port.tcp(443), "Allow from anyone on port 443");
// ALB
const alb = new elbv2.ApplicationLoadBalancer(this, "ALB", {
loadBalancerName: `${serviceName}-alb`,
vpc: vpc,
vpcSubnets: vpcPublicSubnets,
internetFacing: true,
securityGroup: albSecurityGroup,
});
// ALB HTTPS listener
const albListener = alb.addListener("ALBListener", {
protocol: elbv2.ApplicationProtocol.HTTPS,
certificates: [
{
certificateArn: Lazy.string({
produce: () =>
ssm.StringParameter.valueForTypedStringParameterV2(this,
"certificateArn", ssm.ParameterValueType.STRING),
}),
},
],
});
// ALB target group
albListener.addTargets("ALBTarget", {
targetGroupName: `${serviceName}-tg`,
targets: [ecsService],
healthCheck: {
healthyThresholdCount: 3,
interval: Duration.seconds(60),
timeout: Duration.seconds(30),
},
slowStart: Duration.seconds(60),
stickinessCookieDuration: Duration.days(1),
port: containerPort,
protocol: elbv2.ApplicationProtocol.HTTP,
});
// Alias record for ALB
const albARecord = new route53.ARecord(this, "ALBARecord", {
recordName: domainName,
target: route53.RecordTarget.fromAlias(new
route53targets.LoadBalancerTarget(alb)),
zone: route53.HostedZone.fromLookup(this, "HostedZone", {
domainName: env.domain,
}),
});
albARecord.node.addDependency(alb);
流れを整理すると以下のようになります。
コンテナイメージ
- ECR リポジトリを取得
- 前章で紹介した
cdk-docker-image-deploymentを使って ECR へのコンテナイメージのデプロイ
を記述
下準備
- ECS サービスのセキュリティグループやコンテナのポートマッピングで使う情報をオブジェクト
ecsPortSettingsにまとめておく
ECS クラスター
- ECS クラスターを記述
ECS タスク定義
- タスク実⾏ロールを記述
- タスクロールを記述
- タスク定義を記述
- タスク実⾏ロールをアタッチ
- タスクロールをアタッチ
- Keycloak 管理者アクセス⽤のシークレットを記述
- CloudWatch ロググループを記述
ecsPortSettingsからポートマッピング情報を作成- タスク定義にコンテナ情報を追加
- コンテナイメージ情報を記述
- Keycloak ⽤シークレットをアタッチ
- CloudWatch ロググループをアタッチ
- 環境変数を記述
- ポートマッピング情報をアタッチ
- タスク実⾏ロールに DB シークレットの読み取り権限を付与
- タスク実⾏ロールに Keycloak 管理者アクセス⽤シークレットの読み取り権限を付与
ECS サービス
- ECS サービスのセキュリティグループを記述
- ECS サービスを記述
- アタッチする ECS クラスターを渡す
- タスク定義をアタッチ
- ECS サービスのセキュリティグループをアタッチ
ecsPortSettingsから ECS サービスに接続設定を追加- ECS サービスに DB への接続設定を追加
Auto Scaling
- Auto Scaling 設定を記述
- Auto Scaling 設定に CPU Utilization のトリガーを追加
- Auto Scaling 設定にスケジュールベースのトリガーを追加
Application Load Balancer
- ALB ⽤セキュリティグループを記述
- ALB を記述
- セキュリティグループをアタッチ
- リスナーを追加
- ALB リスナーにターゲットグループを追加
Route 53 A Record
- 向き先を ALB とした A レコード (エイリアス) を記述
構成要素が多岐にわたるのでひとつひとつ理解できていることが重要ですが、裏返せばこういう複雑なリソ
ースを CDK コードで記述することで理解が深まるとも⾔えます (私⾃⾝、書いて覚えたところがあります)
要点としては以下があります。
- ポート情報をあらかじめオブジェクトにまとめておくことで、同じポートを複数箇所で書かなくて済む
ようにしている - 要件に合わせてスケジュールベースの Application Auto Scaling を定義している
- 本番利⽤も視野に⼊れた構成を想定しているため、
aws-ecs-patternsは使わずに L2 コンストラク
トで書いている
最後に踏み台⽤の EC2 インスタンスも⽤意しています。
// Bastion host security group
const bastionSecurityGroupName = `${serviceName}-bastion-security-group`;
const bastionSecurityGroup = new ec2.SecurityGroup(this,
"BastionSecurityGroup", {
securityGroupName: bastionSecurityGroupName,
description: bastionSecurityGroupName,
vpc: vpc,
allowAllOutbound: true,
});
Tags.of(bastionSecurityGroup).add("Name", bastionSecurityGroupName);
// Bastion host
const bastion = new ec2.BastionHostLinux(this, "Bastion", {
instanceName: `${serviceName}-bastion`,
instanceType: new ec2.InstanceType("t3.micro"),
vpc: vpc,
securityGroup: bastionSecurityGroup,
})
// Override role name
(bastion.role.node.defaultChild as iam.CfnRole).roleName = `${serviceName}-
bastion-role`
// Allow bastion host connect to database
dbCluster.connections.allowDefaultPortFrom(bastion, "Allow bastion host
connect to database");
L1 コンストラクトにアクセスし、ロール名を命名ルールに則って上書きしています。
今回 ec2.BastionHostLinux() を使って踏み台ホストを作ってみたのですが、コンテナのデバッグやトラブルシューティングに関しては、⾃分のマシンに session-manager-plugin をインストールして直接ECS Exec する⽅式でいい気がしています。
⼀⽅で DB へのアクセスに関しては、Keycloak の DB スキーマをカスタマイズしているようなケースでは必要だと思いますが、そうでない場合は踏み台⾃体が必要ないケースも出てきそうです。このあたりはユースケースによると思います。
余談ですが、Aurora サーバーレス V1 の頃には Query Editor という、マネコンからクエリを発⾏できる機能があって便利だったのですが、V2 ではなくなってしまいました。
デプロイ
ローカルで Docker が起動していることを確認し、以下のコマンドを実⾏します。問題がなければ、
Quarkus-based Keycloak コンテナイメージのビルドおよびデプロイ、ACM 証明書のデプロイ、VPC の構
築、Aurora サーバーレス V2 の構築、Keycloak の搭載された ECS on Fargate の構築、踏み台⽤ EC2 イン
スタンスの構築が⼀挙に⾏われます。
# CFn テンプレート作成 npx cdk synth --all # デプロイ npx cdk deploy --all
AWS Secrets Manager から取得したシークレットで Keycloak 管理者画⾯にログインできることを確認します。
おわりに
CDK を⽤いて OSS の IAM ソフトウェアである Keycloak を構築する⼿順について、背景や留意事項を踏
まえて紹介しました。少し改良すれば、本番環境でも活⽤できると思います。
AWS 環境において、⼤規模でマルチテナントなアプリケーションの認証認可基盤を検討する際、Amazon
Cognito がフィットしないケースでは Keycloak はファーストチョイスになり得ます。そういったケースで
役⽴てば幸いです。



